What Effects the Cost of Floating Solar Energy?
- samialhelali
- Jul 30, 2020
- 4 min read
Updated: Apr 2, 2021
The effect of PV Module Power and Layout Configuration
Floating PV is the installation of PV modules on floating structures on water surface. Floating PV start as an academical research in 2007 and quickly developed into an economically viable and tempting solution. The global installed floating PV capacity increased from 68 MW in 2015 to over 2.1 GW by the end of 2019. Floating PV is expected to account for 2% of total solar PV installations globally in the upcoming 3 years and it is considered the fastest-growing type of solar PV installations and will soon become a pillar of the solar PV industry.
The floating PV industry have emerged fast and is still developing quickly bringing not only new technologies and advancements but also bringing uncertainty and confusion due to the lack of well-established technical standards. The same applies to the price levels of floating solar.
The world bank group in their recently published a report about the floating solar industry has estimated the cost of floating mounting structure for a 50 MWp floating PV power plants as 0.15 $/Wp.
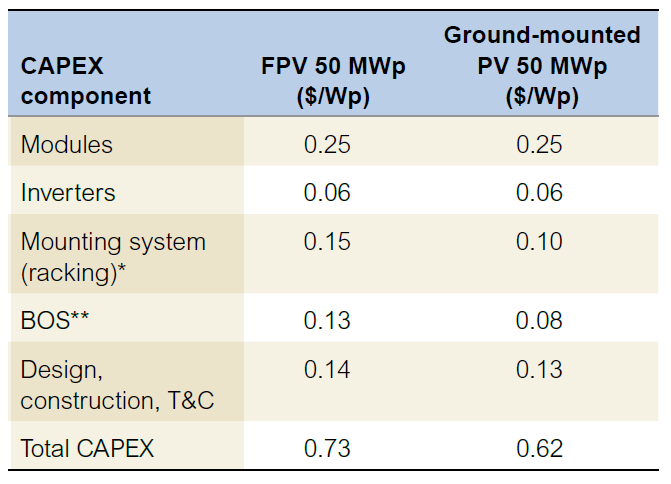
Source: World Bank Group, ESMAP and SERIS. 2019. Where Sun Meets Water: Floating Solar Handbook for Practitioners. Washington, DC: World Bank
However, the cost the floating mounting structures and anchoring and mooring system is very dependent on the site conditions and project specifications and varies significantly from project to another.
This article discusses the effect of PV module power rating and different layout configurations on the cost of the floating mounting structure.
Effect of PV Module Power Rating
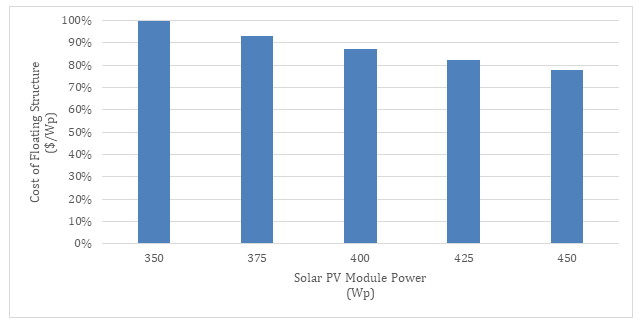
The effect of the power rating of the solar PV module on the Balance of System costs has been known in the solar PV industry for a long time. This applies to the floating mounting structure. The higher the power rating of the solar PV module is, the lower the $/Wp unit cost of the floating mounting structure.
According to detailed layout drawings it is calculated that the cost of HydroSolar V4, TYT’s latest floating mounting structure product decreases by 22% when the solar PV module power rating is increased from 350Wp to 450Wp. The figure below shows the effect of the solar PV module power rating on the cost of HydroSolar floating structure.
Floating Structure Layout Configurations
HydroSolar floating structure is made from modular floats that can be connected to each other in different configurations resulting in different system layouts. The resulting layouts have different characteristics in terms of the number of floats used per PV module, inter PV modules shading, and azimuth angle orientation.
The most used layout configurations are as follow:
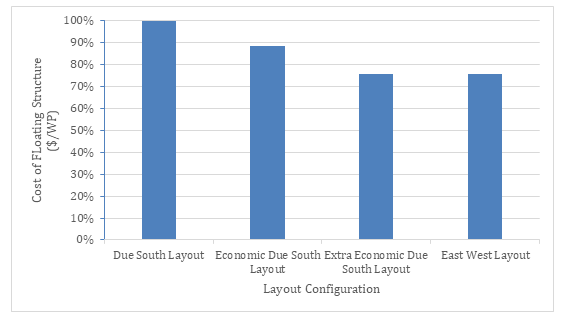
Due South Layout: In this configuration, the PV modules are all facing one azimuth angle orientation, typically south/north. And there are alternating rows of Panel Carrier Floats and Walkway Floats. This configuration provides the maximum durability and easiest access for O&M.

Economic Due South Layout: In this configuration, the PV modules are all facing one azimuth angle orientation, typically south/north. And there are alternating rows of Panel Carrier Floats and Walkway Floats. However, half of the walkway floats use alternative floats to reduce the cost. This configuration provides a relatively lower durability and access to O&M compared to the regular Due South Layout.

Extra Economic Due South Layout: In this configuration, the PV modules are all facing one azimuth angle orientation, typically south/north. And there are is a row of Walkway floats after every two rows of Panel Carrier Floats. This significantly reduces the cost compared to the regular due south configuration. This configuration provides a relatively access to O&M and has a higher inter PV module shading compared to the regular Due South Layout.

East-West Layout: In this configuration, half of the PV modules face one azimuth angle while the other half faces the opposite direction, typically east-west. And there are is a row of Walkway floats after every two rows of Panel Carrier Floats. This significantly reduces the cost compared to the regular due south configuration. This configuration provides a relatively lower and access to O&M and results in a relatively lower amount of solar irradiation incident on the PV module.

The ultimate decision on selecting the optimal layout configuration depends on the site conditions like latitude and project conditions like the economical structure of the project which might prefer a tradeoff of a lower CAPEX and a slightly lower energy yield.
Effect of Layout Configuration
According to detailed layout drawings it is calculated that the cost of HydroSolar V4, TYT’s latest floating mounting structure product varies by up to 24% for different layout configurations. The table below shows the performance of different layout configurations in terms of $/Wp cost.
In summary, the use of PV modules with a higher rating and the selection of the optimal floating structure layout configuration are crucial factors that significantly affect the cost of the floating structure.
Further falls in the floating structure costs are expected in the near future, as 500Wp+, 78 cell PV modules become the PV industry’s norm. Floating system suppliers will adapt there floating system designs to accommodate the larger PV modules and further increase the viability of this green climate-friendly source of energy.




Comments